Abstract: 数字图像处理:第30天
Keywords: 图像平滑,中值滤波
本文最初发表于csdn,于2018年2月17日迁移至此
开篇废话
开篇废话是中值滤波原理和基础代码都很好理解和编写,但是快速算法有点不好写,上周日看了下算法大概的思路然后就开始写,写了一天也不好,周一又调试了一上午,后来发现整个算法其实原理上没有任何难点,只是自己还没完全清楚每个细节就开始写代码,而且算法又是迭代的,一步有问题后面结果都不对,所以,下次再实现算法的时候,要先想一段时间,然后再实现,这样不仅不浪费时间反而可以节约时间,并且不会受到打击。
中值滤波介绍
中值滤波时典型的非线性方法,与前面介绍的方法不同,中值滤波更接近于灰度图像的腐蚀和膨胀,是在一定区域内比较大小,找出中值,也就是排序后中间那个数,也就是中学的中位数,平均数用于均值滤波,中位数用于中值滤波,要是专家就可以写本书:统计学在图像处理中的二三事(这句话属于扯淡)。
中值滤波会产生对原始图像的人为因素破坏,所以在医疗成像等对人为因素引起误差不能够接受的时候不能是用中值滤波。
中值滤波对椒盐噪声和斑点噪声效果显著,而且中值滤波具有较好的边缘保持特性,所以在图像处理中知名度很高。
数学原理
中值滤波的数学公式就是:
$$
g(x,y)=Median{f(x-m/2,y-n/2)\dots f(x+m/2,y+n/2)}
$$
翻译成自然语言就是在当前模板覆盖范围内需找中位数作为结果。
此计算中涉及到排序,所以,如果使用比较的方法排序,最快速度的复杂度是 $O(m\times n\times log(m\times n)\times W\times H)$ ,如果使用非比较型排序,算法最大时间复杂度是 $255\times W\times H$ 也就是 $O(W\times H)$ 但要使用更多的存储空间,最直观的方法是使用计数排序,建立一个255大小的空间,或者理解为一个直方图,来查找中值。
快速方法是使用计数排序,但存在一个类似于游标的指针,指向当前的中值,并记录当前模板覆盖范围内小于中值的数据的个数,当模板滑动的时候,观察移出数据和移入数据对小于中值个数的影响确定移动游标的方向,以此来减少直方图搜索范围,降低运算量。
快速算法
- 初始化 $T=模板覆盖区域元素个数/2$
- 首先,初始化直方图,将该行第一组模板覆盖的元素排序,找出中值 mid_value ,记录小于此中值的元素个数c。
- 移出模板覆盖区域最左侧一列元素,对于每一个元素如果小于 mid_value ,$c=c-1$ ;
- 移入模板覆盖外最右侧一列元素(相当于模板右移), 对于每一个元素如果小于 mid_value ,$c=c+1$ ;
- 比较c和T的大小:
- 如果 $c<T$ :从 mid_value 开始,包括mid_value,向更大的方向检索,如果有搜索到元素,c加上对应的个数,直到 $c\geq T$ ,当前元素为新的 mid_value;
- 如果 $c==T$ :从mid_value开始,包括mid_value,向更大的方向检索,如果有搜索到元素,该元素为新的mid_value;
- 如果 $c>T$ :从mid_value开始,包括mid_value,向更小的方向检索,如果有搜索到元素,c减去对应的个数,直到c<=T,当前元素为新的mid_value,c的值加上新mid_value的个数;
- 如果模板右边无数据,到下一行,回到第2步否则回到第3步,继续;
原型算法代码
1 | //以下为低速普通中值滤波,排序使用计数排序 |
快速算法代码
1 | int findMedian(int *hist,int *movein,int *moveout,int movesize,int *cursor,int median,int t){ |
效果
来观察下lena图矩阵原版的中值滤波结果:
原图数据: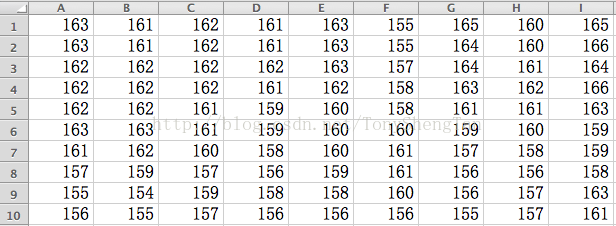
我们的慢速结果: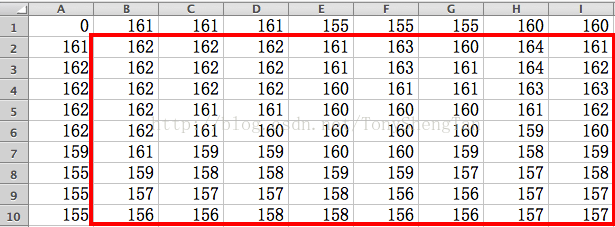
我们的快速结果: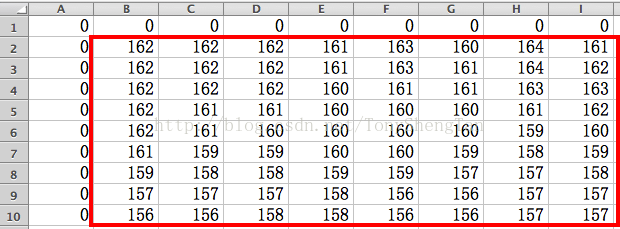
OpenCV的结果: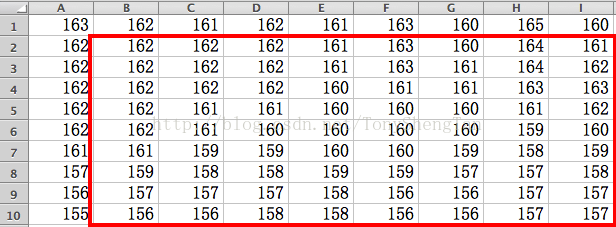
下面看加了椒盐噪声的lena图的中值滤波和高斯滤波的效果: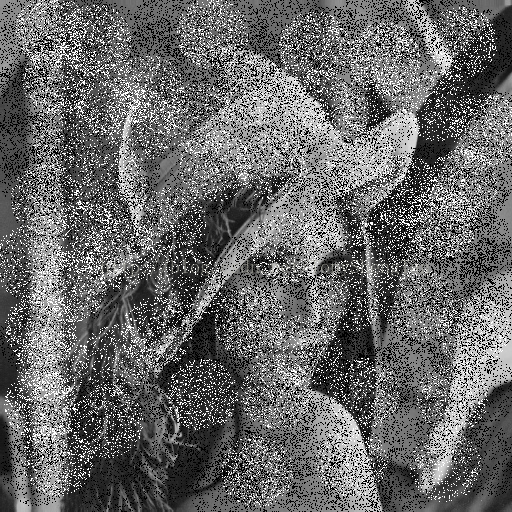
3x3中值: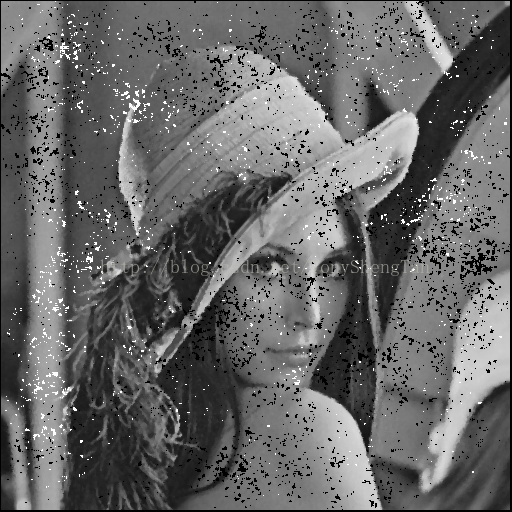
3x3高斯: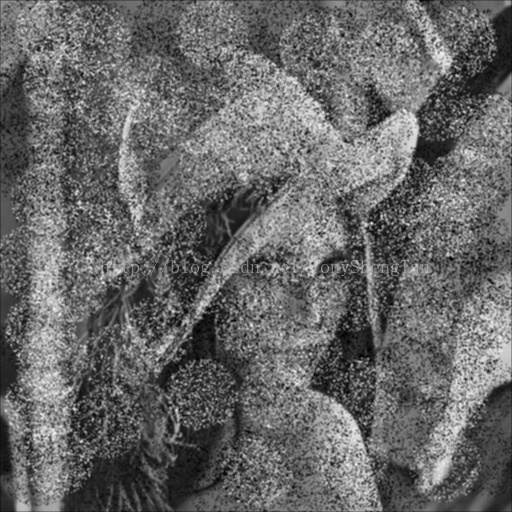
5x5中值: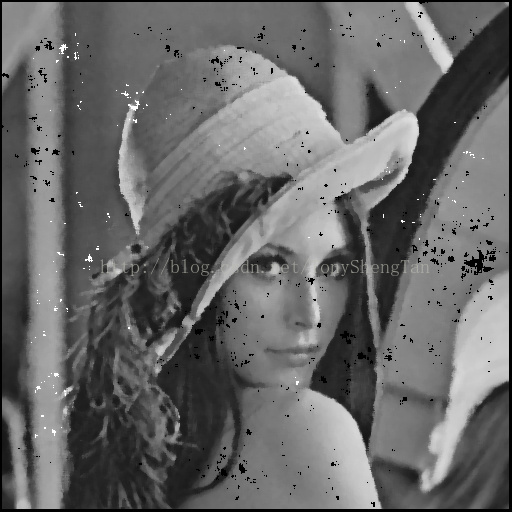
5x5高斯: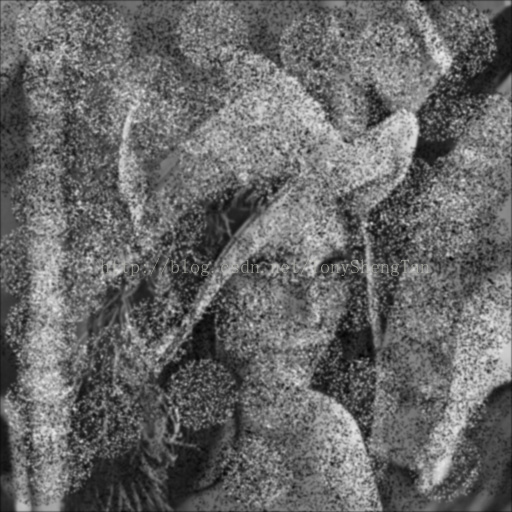
7x7中值: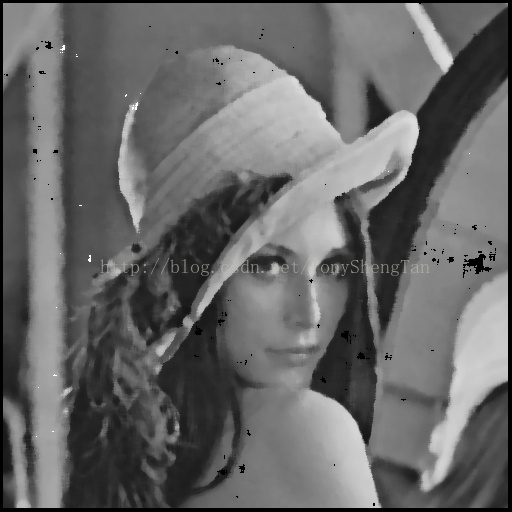
7x7高斯: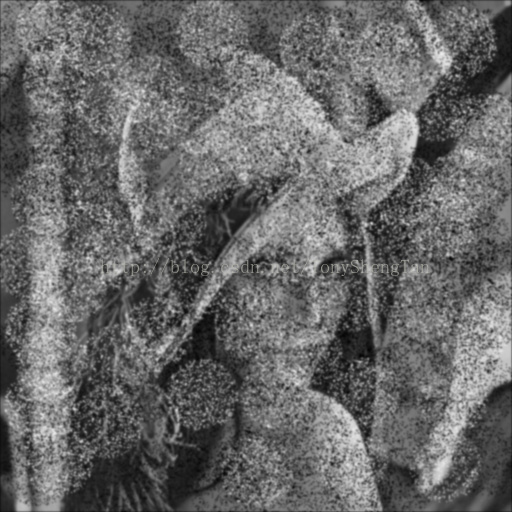
观察结果:对于椒盐噪声影响严重的图片,中值滤波效果远远好于高斯滤波,中值滤波的模板越大图像被模糊的越严重
总结
图像增强基础的平滑算法就介绍到这里,下一篇开始介绍锐化相关
